
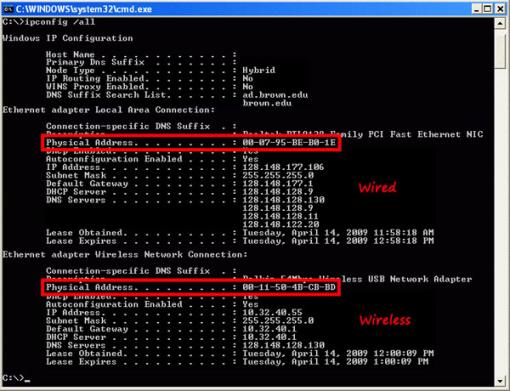
Your router is basically trying to resolve (find) the physical address of which computer this IP address belongs to. So, the router sends an ARP broadcast request on the LAN. When you router wants to send data packets to your computer with IP address ‘X’, the router needs to know what your computers MAC address is. If your computer has two Ethernet ports and dual-band wireless, it will have four MAC addresses. If it has dual-band wireless capability, it will have a MAC address for each wireless band. If the computer has two Ethernet ports, it will have a MAC address for each Ethernet port. Each network controller has its own MAC address. If you do not see your operating system listed, refer to your device’s user manual or product support website.In the previous image, I have one Etherent controller, and one wireless controller. If this does not work, refer to your device’s user manual. In most cases, you can follow this procedure to locate your MAC address:Ī WiFi Address or WiFi MAC Address displays. This is your device’s MAC address.Ī Wi-Fi Address displays. Select Apple Icon > System Preferences > Network > Advanced.Ī WiFi Address or Airport Address displays.

This is your computer’s Ethernet MAC address. Under Ethernet adapter Wireless Network Connection, a Physical Address displays. In the command prompt, type ipconfig /all.The physical address is your device’s MAC address. Click Windows Start or press the Windows key.Ī physical address displays for each adapter.You can block or allow service to a specific device if you know its MAC address. If your computer has multiple network adapters (for example, an Ethernet adapter and a wireless adapter), each adapter has its own MAC address. Follow the steps for the operating system that you use.Įxample of a MAC address: 00:00:00:a1:2b:ccĮvery device connected to your home network has a unique MAC address. Follow these instructions to find your computer or mobile device’s media access control address (MAC address).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
